
If you’re trying to improve your website’s visibility on search engines, you’ve likely heard about On-Page SEO. But what exactly is it, and why is it so crucial for your digital success?In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the meaning of On-Page SEO, break down its core elements, and provide actionable strategies to help your website rank better and attract the right audience.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO (also known as on-site SEO) refers to all the actions you take directly within your website to improve its position in search engine rankings. This includes optimizing your content, improving HTML source code, enhancing user experience, and more.
Unlike off-page search engine optimization (which entails inbound links and external alerts), On-site seo is absolutely under your control. That’s what makes it powerful—you can start optimizing today without waiting for outside help.
Why On-Page SEO Matters
Search engines like Google want to deliver the best, most relevant results to users. On-Page SEO helps search engines:
- Understand your content.
- Evaluate whether it matches a user’s search intent.
- Determine the quality and trustworthiness of your page.
Without proper On-Page optimization, even the most informative content may never reach its intended audience.
Core Elements of On-Page SEO
Let’s dive into the essential components you must focus on when optimizing your web pages.
1. Title Tags
Your page title is the primary element customers see on seek engine results pages (search engines like Google). It should be:
- Clear and concise.
- Include your primary keyword.
- Ideally under 60 characters.
Example:

2. Meta Descriptions
Although it is no longer a direct rating issue, meta descriptions still influence click-through rates.
- Include your main keyword.
- Stay within 155–160 characters.
- Offer a summary that entices users to click.

3. URL Structure
An easy, readable URL improves search engine optimization, and people agree with it.
Bad:
www.example.com/page123?id=abc
Good:
www.example.com/on-page-seo-guide

Make sure to apply hyphens in place of underscores and maintain URLs quickly.
4. Headings (H1, H2, H3…)
Structure your content with proper headings. Your H1 should contain the page’s main topic. Use H2s and H3s for supporting topics.
Well-structured headings:
- Make content scannable for users.
- Help search engines understand your content hierarchy.

5. Keyword Usage
Naturally integrate your focus keyword (“On-Page”) throughout your content:
- In the first 100 words.
- In subheadings (where appropriate).
- Sparingly in body text (avoid keyword stuffing).
- In image alt tags and file names.

6. Content Quality
Content remains king. Your On-Page content should be:
- Original and valuable.
- Clearly address the user’s intent.
- Long enough to cover the topic comprehensively (like this 1500-word guide!).
Use multimedia (images, videos, graphs) where relevant to enhance understanding and engagement.
7. Internal Linking
Link to other relevant pages on your website. For example, if you have a post about Off-Page SEO, link to it from this article. Internal links help:
- Improve crawlability.
- Distribute page authority.
- Keep users on your site longer.
8. Image Optimization
Images should be:
- Compressed for faster load times.
- Named with descriptive filenames.
- Accompanied by alt text using keywords.
Example:
on-page-seo-infographic.jpg
Alt: “On-Page SEO elements diagram”
9. Mobile Responsiveness
Over 60% of net internet site traffic comes from cellular gadgets.
- Display correctly on all screen sizes.
- Use mobile-friendly navigation.
- Pass Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.

Google uses mobile-first indexing, so cellular optimization is no longer optional available—it’s crucial.
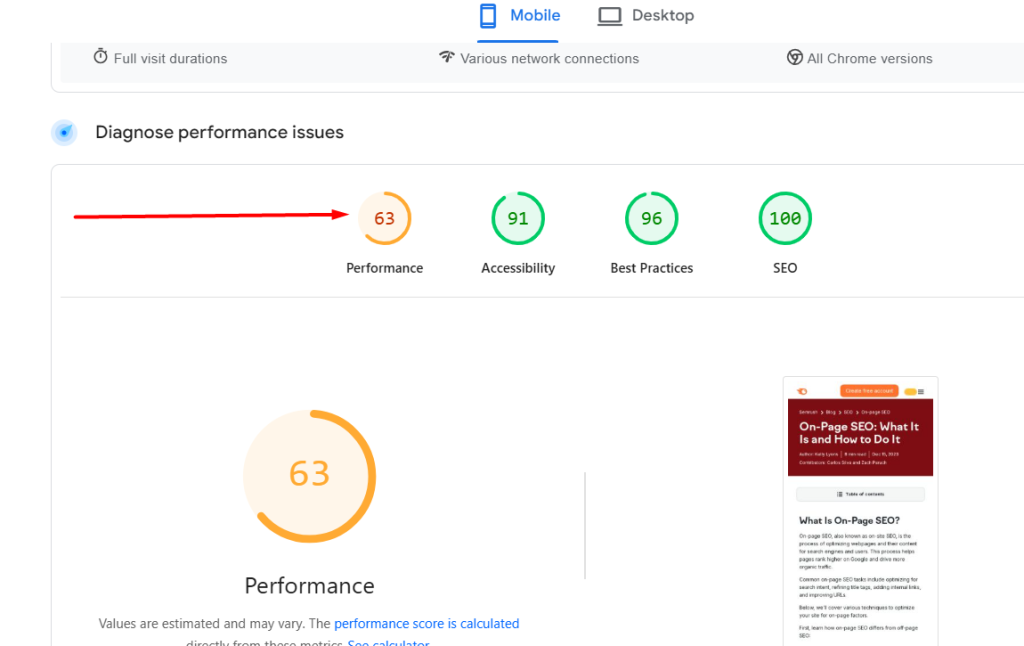
10. Page Speed
Fast-loading websites improve user experience and reduce bounce rates. Use tools like:
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- GTmetrix
- Lighthouse
Tips to improve speed:
- Compress images.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML.
- Use a fast hosting provider and CDN.
11. Schema Markup
Schema (structured data) helps search engines understand your content type. It can enhance your listing with rich results like ratings, reviews, and FAQs.
Use Schema.org to find markup for:
- Articles
- Products
- Local Businesses
- FAQs
- Events
12. User Experience (UX)
Google favors sites that users find easy to use. UX elements include:
- Easy-to-read fonts
- Clear call-to-actions (CTAs)
- Simple navigation
- Accessible design
Happy users mean longer time on site, more engagement, and better rankings.
Common On-Page SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced marketers can slip up. Right here are common mistakes to look at out for:
- Keyword Stuffing: Using your keyword too often hurts readability and SEO.
- Missing Alt Tags: Unoptimized images are a lost opportunity.
- Duplicate Content: Repeating content across pages can hurt your SEO.
- No Internal Linking: You’re not helping search engines or users navigate your site.
- Ignoring Mobile Users: A desktop-only design is outdated and risky.
Advanced On-Page SEO Tips
Want to go beyond the basics? Try these pro-level strategies:
LSI Keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing)
Use related terms around your main keyword to show depth. For “On-Page SEO”, related terms include:
- content optimization
- meta tags
- keyword density
- HTML improvements
Content Refreshing
Update your content regularly. Google loves fresh information. Revise stats, improve readability, and add new examples.
Use Heatmaps
Tools like Hotjar show how users have interacted with your pages. Use these insights to improve layout, CTA placement, and navigation.
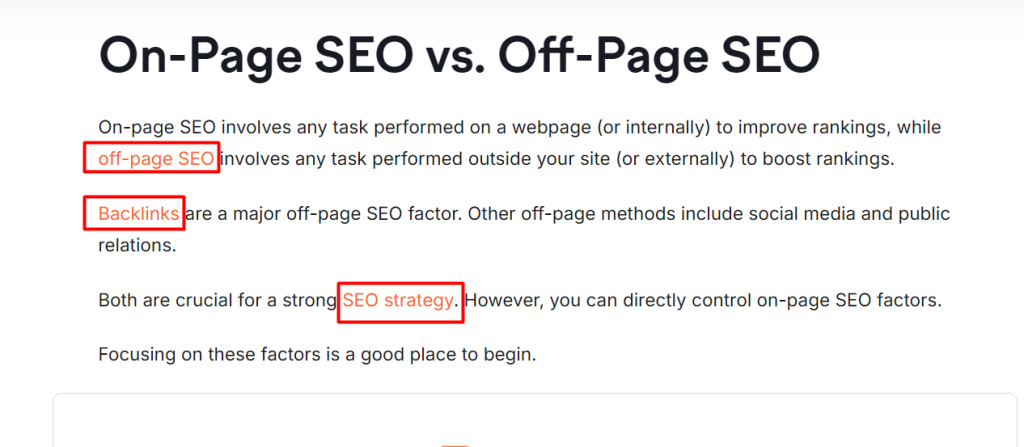
On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO
| Feature | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO |
| Control | 100% controlled by you | Relies on external sources |
| Examples | Titles, content, speed, structure | Backlinks, social signals, mentions |
| Purpose | Help Google understand your site | Build site authority |
For best results, combine both strategies.
How to Measure On-Page SEO Success
After applying these techniques, you’ll want to monitor progress. Use tools like:
- Google Search Console – Track impressions, clicks, and positions.
- Google Analytics – Measure bounce rate, and conversions.
- Ahrefs/SEMrush – Analyze keyword rankings and site health.
Keep an eye on keyword movements and adjust your On-Page elements based on performance data.
Final Thoughts: Master On-Page, Master SEO
in the international of seo, on-page seo is your foundation. It gives your website the structure and clarity it needs to be found, understood, and trusted by both users and search engines.
If you’re just starting out, don’t feel overwhelmed. Focus on the basics—clear titles, great content, fast loading times—and build from there. As your skills grow, incorporate schema markup, A/B testing, and advanced UX improvements.
Remember, On-Page SEO is not a one-time job. It’s an ongoing technique of improvement, optimization, and boom. Keep refining your content and structure, and you’ll see better results over time.
